What is Blockchain Technology – A Quick Overview

Enterprise blockchain technology is becoming increasingly popular among firms seeking transparency and security. Organizations are looking for a concise blockchain description to help them grasp the upcoming “distributed ledger” technology. Here’s what smart businesses should understand about what it is, why it matters, and how it works.
What is Blockchain Technology?
It’s a type of database technique that keeps data in blocks connected together in a chain. It maintains chronological consistency and enables more transparent information sharing across a network of organizations.
Its services assist businesses in avoiding unauthorized financial transactions by using a decentralized recording system that requires both parties to approve each transaction before financial information is automatically updated in their separate ledgers. A blockchain network can also be used to build a secure, immutable record for more efficient and secure order tracking, payment management, and account updates.
This technology provides a few key characteristics to help organizations better trace transactions and increase overall data transparency:
- Immutable shared ledgers improve visibility and cohesiveness in corporate transactions.
- Established guidelines for participant permission to record financial transactions.
- Decentralized networks maintain balanced system controls.
Why is Blockchain important?
Blockchain is important to security. Here is why. New blocks with new information are constantly added to the end of the chain. Each addition has its own digital signature, or hash, which is a string of numbers and characters. “Consider a secret math code. Change the quantity or number in the block after it has been inserted, and the signatures will also change.”
To succeed, hackers must accurately update all of the information up and down the blockchain.
This technology also eliminates middlemen, enabling firms to reduce costs while increasing profits. This enables businesses to validate and execute safe transactions more directly. In theory, transactions can be completed without the use of attorneys, bankers, brokers, or other intermediaries. And they are completed in a more engaging manner since data modifications can be made by anyone along the chain and then viewed and confirmed by other participants.
“The momentum for blockchain technology is clearly building, with Gartner estimating it will generate 3.1 trillion in business value by 2030.”
How does Blockchain Technology work?
Understanding the community nature of blockchain helps clarify how it functions best. It is based on distributed ledger technology (DLT). Everyone in the peer-to-peer network that forms these ledgers can see the same information in individual blocks.
A transaction logged on one computer or node is visible to all computers on the digital network. Everyone can view the same information. Furthermore, they have the ability to reject or confirm their findings. The information is subsequently related to each subsequent block in the chain.
This is what makes the technology so tough to hack. No one computer controls the data, and changing it in one block would require the entire chain to follow suit. Everyone has a copy that is automatically updated; changes must be validated by everyone on the network.
What are the four types of Blockchain Networks?
There are four sorts of blockchain networks: semi-private, private, public, and consortium. Let’s take a deeper look at each network.
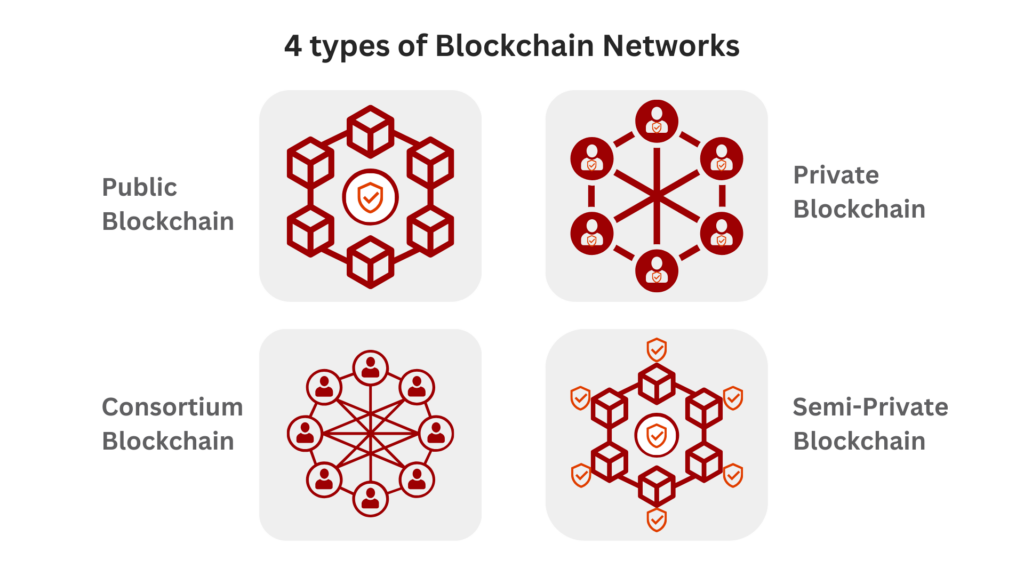
1. Semi-Private Blockchain
It is maintained by a single entity, and access to transaction data is limited to people who match certain conditions. These are referred to as “permissioned” because they require users to provide particular rights in order to access certain transaction data or records inside the business network. These are most commonly used in government and B2B transaction networks.
2. Private Blockchain
These are also administered by a single entity, but they are completely centralized inside the corporate network. A private platform determines who has access to certain information, how transactions are filed, and who can participate in the consensus process. Due to their centralized nature, private blockchains are frequently used as test environments rather than actual network production.
3. Public Blockchain
These networks, such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, are “permissionless,” which means that all transactions on the network are visible to the public. With public networks, anybody can access the blockchain, participate in the consensus process, and add transactions to the record while remaining anonymous.
4. Consortium Blockchain
As the most well-recognized models, consortium blockchains not only help with consensus procedures by identifying pre-selected participants, but they also enable both public and limited access controls. These are “permissioned,” which implies that corporate users must have access to the network before they can view, read, or submit transactions.
What are the key benefits of using blockchain?
- Blockchain technology has a variety of advantages for companies due to its transparency and immutability.
- Transparency: Its data is visible to all parties and cannot be changed. This reduces risk and fraud while increasing trust.
- Security: The dispersed and encrypted characteristics make it difficult to hack. where it has the ability to improve the corporate and IoT security of your business.
- Fewer intermediaries: The peer-to-peer network reduces the need for third-party middlemen. This improves operations efficiency, resulting in fewer data input errors and transaction costs.
- Traceability: Immutable data enables monitoring and tracing of items or their origins throughout complex supply chains.
- Increased efficiency and ROI: Distributed ledgers will provide immediate ROI by assisting firms in developing more efficient and profitable operations.
- Faster processes: It can accelerate process execution in multi-party contexts, allowing for speedier transactions that are not constrained by office hours.
- Automation: It is programmable, which allows it to automatically initiate actions, events, and payments when particular conditions are satisfied.
- Data Privacy: While information is validated and uploaded to the network via a consensus mechanism, a hash code converts the data into a series of letters and numbers. Participants in the network have no means of interpreting such information without a key.
Conclusion:
Now that we have introduced you to the basics of blockchain and its importance in business, it’s time to get deeper into its potential and the many ways that it can drive to optimize your business.
So, why wait? Connect with us, we KaarTech has over 20 years of expertise in delivering and integrating ERP software, including SAP’s Clean Core with AI, RPA, and Blockchain technologies for customers globally. We set ourselves apart as a leader who is used to making a difference in your business rather than just turning up.
Are you excited to know more? Check out the following link to find out: SAP Blockchain Technology – A New Future for SAP
FAQ’s
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology organizes data into interconnected blocks, resulting in a secure and transparent ledger. It maintains chronological consistency and allows for transparent information sharing across a network of organizations.
How does blockchain work?
It is based on distributed ledger technology (DLT), in which every participant is connected to a peer-to-peer network and has access to the same information in individual blocks. Transactions are accessible to all network participants, and modifications need consensus throughout the whole network, making it highly secure and resistant to hacking.
What are the benefits of blockchain?
It provides transparency, security, and immutability. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, improves traceability in supply chains, boosts efficiency and return on investment (ROI), speeds up operations, allows automation, and protects data privacy through encryption.
How does blockchain affect enterprise resource planning (ERP)?
Blockchain-based ERP marks a substantial shift in the management of company data and operations. It improves efficiency, traceability, and automation by utilizing blockchain’s core qualities such as transparency, security, and immutability.
