The Essentials of Process Manufacturing in SAP PP

Greetings, dear readers!
Welcome to another exciting journey into the world of SAP PP. In today’s blog, we’re about to embark on a fascinating exploration of the SAP PP module, with a special focus on process manufacturing. But before we dive in, have you checked out our previous blog on “Discrete vs Repetitive vs Process Manufacturing in SAP PP“? It’s a must-read if you’re into production planning!
Understanding Process Manufacturing in SAP PP
Process manufacturing in SAP PP is a cornerstone of industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage. Unlike discrete manufacturing, which produces individual items, process manufacturing focuses on the creation of products through continuous or batch-oriented processes. This approach ensures the production of consistent and high-quality goods.
Key Features and Benefits of Process Manufacturing in SAP PP
Now, let’s talk about the magic ingredients of SAP PP in process manufacturing:
- Recipe Management:
SAP PP excels in managing complex recipes or formulas. These recipes can include multiple ingredients with specific proportions. This feature is invaluable for industries that demand precise production planning and execution. It helps ensure that the right ingredients are used in the right quantities.
- Batch Management:
Process manufacturing often involves working with batches of materials. SAP PP enables efficient batch tracking throughout the manufacturing process. This includes tracking raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods, ensuring complete traceability. It also facilitates compliance with strict regulatory requirements, which is critical for industries like pharmaceuticals.
- Yield Management:
Maximizing yield while minimizing waste is a key concern for process manufacturers. SAP PP offers tools for monitoring and optimizing yield throughout the production process. This not only reduces costs but also maximizes overall productivity, making it an indispensable feature for businesses.
- Quality Control:
Ensuring that products meet specified quality standards is paramount in process manufacturing. SAP PP provides a comprehensive quality control system. It allows businesses to perform thorough quality checks on raw materials, intermediates, and finished products, guaranteeing that only products meeting the defined standards proceed further in the production process or for distribution.
Production Methods in Process Manufacturing
Process manufacturing can be split into two production methods:
➔ Continuous Process Manufacturing
➔ Batch Process Manufacturing
- Continuous Process Manufacturing:
Continuous process manufacturing is similar to repetitive manufacturing in the sense that it never ends. The method is committed to a specific production rate, producing the same product year-round with minimal setup requirements and little change over time. Intermediate products continuously move from one step to the next, enabling flexibility to adjust operation speeds and output to meet market demands. This method is commonly used for chemical compounds, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
- Batch Process Manufacturing:
Unlike continuous manufacturing, batch process manufacturing depends on customer demand, making it a custom manufacturing approach. It involves producing finite quantities measured either by mass or volume. Once a batch is complete, equipment is cleaned and prepared for the next batch, making it ideal for customized products but less suitable for high-volume production.
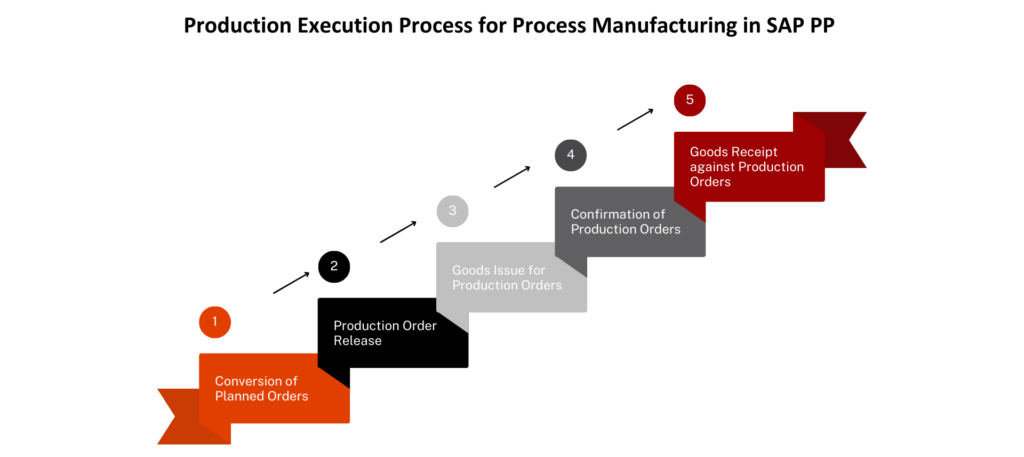
Production Execution Process for Process Manufacturing in SAP PP
Now, let’s peek behind the scenes of the production process:
- Conversion of Planned Orders:
The journey begins with planned orders generated through material requirement planning. These orders are then transformed into production orders, which are the foundation for executing the manufacturing process.
- Production Order Release:
Once production orders are in place, they are released for execution. This step signifies the green light for the manufacturing process to begin.
- Goods Issue for Production Orders:
Raw materials and components required for production are issued from the inventory to the production orders. This is where materials are allocated to specific production processes.
- Confirmation of Production Orders:
As production proceeds, operators confirm the completion of each operation. This real-time confirmation ensures accurate tracking of work progress and helps maintain production efficiency.
- Goods Receipt against Production Orders:
After the production process is complete, finished goods are received into inventory. This marks the end of the manufacturing journey, with products now ready for further processing or distribution.
But wait, there’s more!
SAP PP isn’t one-size-fits-all. It’s like a versatile actor that adapts to different roles. Industries like pharmaceuticals or food and beverage each have their unique needs. SAP PP can configure itself to meet those special requirements.
Interested in learning how SAP PP can adapt to various industries? Click here to explore its versatility in meeting unique manufacturing requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SAP PP is a robust module that empowers process manufacturers to optimize their production processes, maintain strict quality control, and achieve operational efficiency. By grasping the fundamentals of process manufacturing in SAP PP, businesses can drive growth and success within their respective industries. This module serves as the backbone for industries where precision, quality, and efficiency is paramount.
So, stay tuned for more insightful journeys with us! Until next time, keep innovating and optimizing! Contact us to know more..
FAQ’s
What is the primary focus of process manufacturing in SAP PP?
Process manufacturing in SAP PP is primarily focused on industries such as chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage, where the production involves continuous or batch-oriented processes to create consistent and high-quality products.
How does SAP PP support process manufacturing?
SAP PP offers key features like recipe management, batch management, yield management, and quality control to help industries manage complex formulas, track materials throughout the production process, optimize yield, and ensure product quality.
What are the two production methods in process manufacturing?
Process manufacturing can be categorized into continuous process manufacturing, which produces the same product year-round with minimal setup, and batch process manufacturing, which is custom manufacturing based on customer demand and involves finite quantities and cleaning equipment between batches.
What are the key steps in the production execution process for process manufacturing in SAP PP?
The production execution process in SAP PP includes the conversion of planned orders into production orders, the release of production orders, goods issue for production orders to allocate materials, confirmation of production orders to track work progress, and goods receipt against production orders to mark the completion of the manufacturing process.